2711.Arrays
Time Limit: 1s Memory Limit: 256MBYou are given two arrays A and B consisting of integers, sorted in non-decreasing order. Check whether it is possible to choose k numbers in array A and choose m numbers in array B so that any number chosen in the first array is strictly less than any number chosen in the second array.
Input Format(From the terminal/stdin)
The first line contains two integers nA,nB (1 \le nA,nB \le 105), separated by a space - the sizes of arrays A and B, correspondingly.
The second line contains two integers k and m (1 \le k \le nA,1 \le m \le nB), separated by a space.
The third line contains nA numbers a1,a2,... anA (-109 \le a1 \le a2 \le ... \le anA \le 109), separated by spaces - elements of array A.
The fourth line contains nB integers b1,b2,... bnB (-109 \le b1 \le b2 \le ... \le bnB \le 109), separated by spaces - elements of array B.
Output Format(To the terminal/stdout)
Print "YES" (without the quotes), if you can choose k numbers in array A and m numbers in array B so that any number chosen in array A was strictly less than any number chosen in array B. Otherwise, print "NO" (without the quotes).
Hints
In the first sample test you can, for example, choose numbers 1 and 2 from array A and number 3 from array B (1 \lt 3 and 2 \lt 3).
In the second sample test the only way to choose k elements in the first array and m elements in the second one is to choose all numbers in both arrays, but then not all the numbers chosen in A will be less than all the numbers chosen in B: 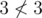 .
.