2714.Minimization
Time Limit: 1s Memory Limit: 256MBYou've got array A, consisting of n integers and a positive integer k. Array A is indexed by integers from 1 to n.
You need to permute the array elements so that value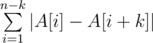 became minimal possible. In particular, it is allowed not to change order of elements at all.
became minimal possible. In particular, it is allowed not to change order of elements at all.
Input Format(From the terminal/stdin)
The first line contains two integers n,k (2 \le n \le 3 \cdot 105, 1 \le k \le min(5000,n-1)).
The second line contains n integers A[1],A[2],...,A[n] (-109 \le A[i] \le 109), separate by spaces - elements of the array A.
Output Format(To the terminal/stdout)
Print the minimum possible value of the sum described in the statement.
Hints
In the first test one of the optimal permutations is 142.
In the second test the initial order is optimal.
In the third test one of the optimal permutations is 234435.
Submit
请先 登录