3170.The Child and Sequence
Time Limit: 1s Memory Limit: 256MBAt the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1],a[2],...,a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following: Print operation l,r. Picks should write down the value of 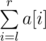 . Modulo operation l,r,x. Picks should perform assignment a[i]=a[i]modx for each i (l \le i \le r). Set operation k,x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k]=x). Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
. Modulo operation l,r,x. Picks should perform assignment a[i]=a[i]modx for each i (l \le i \le r). Set operation k,x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k]=x). Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
Input Format(From the terminal/stdin)
Input The first line of input contains two integer: n,m (1 \le n,m \le 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space: a[1],a[2],...,a[n](1 \le a[i] \le 109) - initial value of array elements.Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 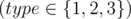 . If type=1, there will be two integers more in the line: l,r(1 \le l \le r \le n), which correspond the operation 1. If type=2, there will be three integers more in the line: l,r,x(1 \le l \le r \le n;1 \le x \le 109), which correspond the operation 2. If type=3, there will be two integers more in the line: k,x(1 \le k \le n;1 \le x \le 109), which correspond the operation 3.
. If type=1, there will be two integers more in the line: l,r(1 \le l \le r \le n), which correspond the operation 1. If type=2, there will be three integers more in the line: l,r,x(1 \le l \le r \le n;1 \le x \le 109), which correspond the operation 2. If type=3, there will be two integers more in the line: k,x(1 \le k \le n;1 \le x \le 109), which correspond the operation 3.
Output Format(To the terminal/stdout)
Output For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
Sample Input 1
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 5 4 3 3 5 1 2 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 3· \n · · · · \n · · · \n · · \n · · \n · · · \n · · \n
Sample Output 1
8 5\n \n
Sample Input 2
10 10 6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5 1 3 9 2 7 10 9 2 5 10 8 1 4 7 3 3 7 2 7 9 9 1 2 4 1 6 6 1 5 9 3 1 10· \n · · · · · · · · · \n · · \n · · · \n · · · \n · · \n · · \n · · · \n · · \n · · \n · · \n · · \n
Sample Output 2
49 15 23 1 9\n \n \n \n \n
Hints
Consider the first testcase: At first, a={1,2,3,4,5}. After operation 1, a={1,2,3,0,1}. After operation 2, a={1,2,5,0,1}. At operation 3, 2+5+0+1=8. After operation 4, a={1,2,2,0,1}. At operation 5, 1+2+2=5.